Defense for Microsoft Active Directory
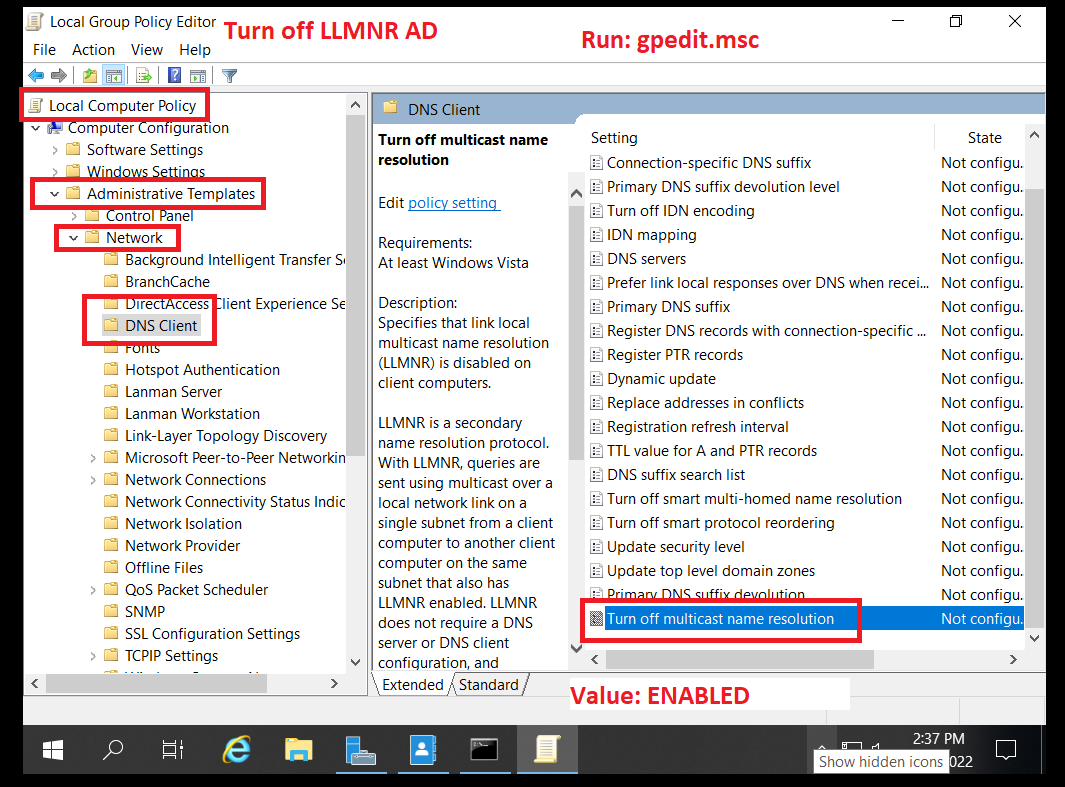
1. Turn off LLMNR
More info: https://www.blackhillsinfosec.com/how-to-disable-llmnr-why-you-want-to/
2. Disable NBT-NS
Disabling the use and support of NetBIOS can help to mitigate an attacker's ability to: poison and spoof responses, obtain a user's hashed credentials, inspect web traffic, etc.
3. Turn on SMB Signing on All Devices
Old article, but still works: https://www.itprotoday.com/security/how-do-i-enable-smb-signing
4. Multiple Steps for Ipv6
1. Disable IPv6 via Group Policy and Firewall. If you disable it completely, it can cause issues.
Recommended: Firewall DISABLE.
- (Inbound) Core Networking - Dynamic Host Configuraiton Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPV6-IN)
- (Inbound) Core Networking - Router Advertisement (ICMPv6-In)
- (Outbound) Core Networking - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPV6-Out)
2. If WPAD is not in use internally, disable it via Group Policy and by disabling the WinHttpAutoProxySvc service.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/windows-server/networking/disable-http-proxy-auth-features3. Relaying to LDAP and LDAPS can only be mitigated by enabled both LDAP signing and LDAP channel binding.
More research on this needed.






Comments
Post a Comment